Rotary Screw Air Compressor 7.5 To 270 HP Lubricated
Main part of Screw Compressor is Air-end, consisting of a pair of rotors. The male motor is driven by electric motor. Suction of air though Inlet filter and suction control valve. Air – oil mixture from air-end flows into an air – oil separator. The separated oil flows through oil filter and after cooling in 'cooler', it gets back into the system. The air also passes through air cooler and to the receiver. The whole system is controlled through valves / sequence of compressor is done through electric /electronic control.





High Quality Compressors

Compact, High-efficiency, Low-noise:
- Big Rotor, Big Output Capacity, Good Specific Power.
- Stable Air Flow Volume, Less wear Parts than Piston Compressor, High Reliability
Low Investments:
- Mechanical structure is simple, has low running cost and provides a continuous 24 hours operation
High Reliability:
- Less moving parts. Integrated combination parts, Lower failure, high protection grade
- Excellent quality compressed air, outlet compressed air oil content less than 3ppm, suitable for all main industry area
Fully Automatic Interlocking Control and Operation Management
Intelligent PLC, with the signals of pressure, temperature, current provided with key important indicator of 12 alarms and full security protection measures, multi-language display suited for different countries requirement, maintenance period reminder, RS485 communications interface help realize linkage work for many compressors, concisely and comprehensively to let customer understand the running situation in a timely manner.
Safe Leakage-Proof Connection

Abandoned the traditional hose with low cost whole rigid line and flexible connection, put an end to bursting of ageing of pipeline causing leakage, reduce the oil pressure loss at the same time. Adopt cutting sleeve or ?uorine rubber o-rings for sealing which prevent leakage. Also, it helps reduce vibration effectively.
Intake Valve With Saving Energy
Intake valve with high-quality and high reliability effectively control the loading and unloading of machine, saving energy. Sol.valve service life is up to 2 million times more than the structure used to upgrade, no gap can be completely sealed, no need air cylinder pneumatic control, no seal diaphragm etc. wearing parts.

Electric control Components
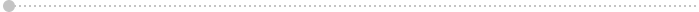

Reliable electrical control components to ensure the long-term stable operation of units.
General Arrangement Diagram of Compressed Air System
Rotary Screw Small Range (7.5 To 30 Hp)
Technical Specifications
| MODEL | 7 BAR | 8 BAR | 10 BAR | 13 BAR | Motor Power HP | Length MM | Width
MM |
Height
MM |
Weight
kg |
Air Conn. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | |||||||
| IAS 7.5 | 0.85 | 30 | 0.79 | 28 | 0.71 | 25 | 0.62 | 22 | 7.5 | 870 | 760 | 1120 | 286 | ¾" |
| IAS 10 | 1.13 | 40 | 0.99 | 35 | 0.91 | 32 | 0.79 | 28 | 10 | 870 | 760 | 1120 | 292 | ¾" |
| IAS 15 | 1.70 | 60 | 1.61 | 57 | 1.42 | 50 | 1.22 | 43 | 15 | 870 | 760 | 1120 | 351 | ¾" |
| IAS 20 | 2.38 | 84 | 2.29 | 81 | 1.98 | 70 | 1.81 | 64 | 20 | 870 | 760 | 1120 | 489 | ¾" |
| IAS 25 | 3.29 | 116 | 3.00 | 106 | 2.61 | 92 | 2.32 | 82 | 25 | 1470 | 1115 | 1175 | 504 | 1 ¼" |
| IAS 30 | 3.77 | 133 | 3.51 | 124 | 3.29 | 116 | 2.89 | 102 | 30 | 1470 | 1115 | 1175 | 517 | 1 ¼" |
| MODEL | IAS 7.5 | IAS 10 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 0.85 | 1.13 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 30 | 40 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 0.79 | 0.99 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 28 | 35 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 0.71 | 0.91 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 25 | 32 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 0.62 | 0.79 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 22 | 28 |
| Motor Power HP | 7.5 | 10 |
| Length MM | 870 | 870 |
| Width MM | 760 | 760 |
| Height MM | 1120 | 1120 |
| Weight kg | 286 | 292 |
| Air Conn. | ¾" | ¾" |
| MODEL | IAS 15 | IAS 20 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 1.70 | 2.38 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 60 | 84 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 1.61 | 2.29 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 57 | 81 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 1.42 | 1.98 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 50 | 70 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 1.22 | 1.81 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 43 | 64 |
| Motor Power HP | 15 | 20 |
| Length MM | 870 | 870 |
| Width MM | 760 | 760 |
| Height MM | 1120 | 1120 |
| Weight kg | 351 | 489 |
| Air Conn. | ¾" | ¾" |
| MODEL | IAS 25 | IAS 30 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 3.29 | 3.77 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 116 | 133 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 3.00 | 3.51 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 106 | 124 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 2.61 | 3.29 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 92 | 116 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 2.32 | 2.89 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 82 | 102 |
| Motor Power HP | 25 | 30 |
| Length MM | 1470 | 1470 |
| Width MM | 1115 | 1115 |
| Height MM | 1175 | 1175 |
| Weight kg | 504 | 517 |
| Air Conn. | 1 ¼" | 1 ¼" |
Rotary Screw Medium Range(40 To 125 Hp)
Technical Specifications
| MODEL | 7 BAR | 8 BAR | 10 BAR | 13 BAR | Motor Power HP | Length MM | Width MM |
Height MM |
Weight kg |
Air Conn. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | |||||||
| IAS 40 | 5.10 | 180 | 4.98 | 176 | 4.19 | 148 | 3.68 | 130 | 40 | 1470 | 1115 | 1175 | 610 | 1 ½" |
| IAS 50 | 6.46 | 228 | 6.29 | 222 | 5.81 | 205 | 5.30 | 187 | 50 | 1450 | 1600 | 1480 | 650 | 1 ½" |
| IAS 60 | 8.13 | 287 | 8.01 | 283 | 6.80 | 240 | 6.00 | 212 | 60 | 1850 | 1600 | 1480 | 1050 | 2" |
| IAS 75 | 10.39 | 367 | 10.00 | 353 | 8.50 | 300 | 7.59 | 268 | 75 | 1850 | 1600 | 1480 | 1250 | 2" |
| IAS 100 | 13.82 | 488 | 13.31 | 470 | 11.70 | 413 | 10.00 | 353 | 100 | 2340 | 1740 | 2000 | 1760 | 2 ½" |
| IAS 125 | 16.51 | 583 | 16.00 | 565 | 14.50 | 512 | 12.52 | 442 | 125 | 2340 | 1740 | 2000 | 1890 | DN 65 |
| MODEL | IAS 40 | IAS 50 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 5.10 | 6.46 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 180 | 228 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 4.98 | 6.29 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 176 | 222 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 4.19 | 5.81 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 148 | 205 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 3.68 | 5.30 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 130 | 187 |
| Motor Power HP | 40 | 50 |
| Length MM | 1470 | 1450 |
| Width MM | 1115 | 1600 |
| Height MM | 1175 | 1480 |
| Weight kg | 610 | 650 |
| Air Conn. | 1 ½" | 1 ½" |
| MODEL | IAS 60 | IAS 75 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 8.13 | 10.39 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 287 | 367 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 8.01 | 10.00 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 283 | 353 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 6.80 | 8.50 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 240 | 300 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 6.00 | 7.59 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 212 | 268 |
| Motor Power HP | 60 | 75 |
| Length MM | 1850 | 1850 |
| Width MM | 1600 | 1600 |
| Height MM | 1480 | 1480 |
| Weight kg | 1050 | 1250 |
| Air Conn. | 2" | 2" |
| MODEL | IAS 100 | IAS 125 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 13.82 | 16.51 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 488 | 583 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 13.31 | 16.00 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 470 | 565 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 11.70 | 14.50 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 413 | 512 |
| 13 BAR M3/ MIN | 10.00 | 12.52 |
| 13 BAR Delivery CFM | 353 | 442 |
| Motor Power HP | 100 | 125 |
| Length MM | 2340 | 2340 |
| Width MM | 1740 | 1740 |
| Height MM | 2000 | 2000 |
| Weight kg | 1760 | 1890 |
| Air Conn. | 2 ½" | DN 65 |
Rotary Screw Large Range (150 To 270 Hp)
Technical Specifications
| MODEL | 7 BAR | 8 BAR | 10 BAR | 12.5 BAR | Motor Power HP | Length MM | Width MM | Height MM | Weight kg | Air Conn. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | M3/ MIN | Delivery CFM | |||||||
| IAS 150 | 20.25 | 715 | 19.97 | 705 | 17.42 | 615 | 15.58 | 550 | 150 | 2340 | 1740 | 2000 | 2350 | DN 65 |
| IAS 180 | 24.5 | 865 | 24.0 | 847 | 21.0 | 741 | 18.00 | 635 | 180 | 2700 | 1750 | 1850 | 3100 | DN 65 |
| IAS 220 | 29.0 | 1024 | 28.3 | 1000 | 24.0 | 848 | 21.5 | 759 | 220 | 2700 | 1750 | 1850 | 3200 | DN 65 |
| IAS 250 | 32.5 | 1147 | 31.6 | 1116 | 28.3 | 999 | 24.5 | 865 | 250 | 2700 | 1820 | 1850 | 3450 | DN 80 |
| IAS 270 | 35 | 1236 | 33.6 | 1186 | 30.8 | 1088 | 27.2 | 960 | 270 | 2700 | 1820 | 1850 | 3600 | DN 80 |
| MODEL | IAS 150 | IAS 180 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 20.25 | 24.5 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 715 | 865 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 19.97 | 24.0 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 705 | 847 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 17.42 | 21.0 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 615 | 741 |
| 12.5 BAR M3/ MIN | 15.58 | 18.00 |
| 12.5 BAR Delivery CFM | 550 | 635 |
| Motor Power HP | 150 | 180 |
| Length MM | 2340 | 2700 |
| Width MM | 1740 | 1750 |
| Height MM | 2000 | 1850 |
| Weight kg | 2350 | 3100 |
| Air Conn. | DN 65 | DN 65 |
| MODEL | IAS 220 | IAS 250 |
|---|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 29.0 | 32.5 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 1024 | 1147 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 28.3 | 31.6 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 1000 | 1116 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 24.0 | 28.3 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 848 | 999 |
| 12.5 BAR M3/ MIN | 21.5 | 24.5 |
| 12.5 BAR Delivery CFM | 759 | 865 |
| Motor Power HP | 220 | 250 |
| Length MM | 2700 | 2700 |
| Width MM | 1750 | 1820 |
| Height MM | 1850 | 1850 |
| Weight kg | 3200 | 3450 |
| Air Conn. | DN 65 | DN 80 |
| MODEL | IAS 270 |
|---|---|
| 7 BAR M3/ MIN | 35 |
| 7 BAR Delivery CFM | 1236 |
| 8 BAR M3/ MIN | 33.6 |
| 8 BAR Delivery CFM | 1186 |
| 10 BAR M3/ MIN | 30.8 |
| 10 BAR Delivery CFM | 1088 |
| 12.5 BAR M3/ MIN | 27.2 |
| 12.5 BAR Delivery CFM | 960 |
| Motor Power HP | 270 |
| Length MM | 2700 |
| Width MM | 1820 |
| Height MM | 1850 |
| Weight kg | 3600 |
| Air Conn. | DN 80 |
What is a screw type air compressor?
Indo-Air’s rotary screw air compressors serve as the backbone of a wide range of industrial applications. The principle of the rotary screw air compressors are made from high-end designs, innovative features, and technologies to provide cost-effective, long-lasting, dependable, and premium compressed air solutions for light to heavy-duty industrial applications.
Rotary screw air compressors are high-efficiency rotary positive displacement machines that can operate at high speeds over a wide range of operating pressures and flow rates. There are no valves or other mechanical forces that can induce unbalance in screw air compressors. This permits a compressor to run at high speeds while delivering a huge flow rate in a tiny package. The fundamental benefit of employing a rotary screw air compressor is that it can continuously produce compressed air with little delivery pressure fluctuations and generates less heat than traditional air compressors, resulting in energy efficiency.
How does a screw type air compressor work?
Within the casing of a rotary screw air compressor, two interlocked helical rotors rotate in opposite directions. Ambient air is drawn into the compressor and circulated through the intended valve, where it is confined between the two helical rotors. As the screws turn, the pressure rises as the air volume decreases. Inside a rotary screw air compressor, Lysholm screws can be found.
Air compressors, in many circumstances, will have the full power of two screws, which is necessary for many large-scale productions. Some rotary screw air compressors only have one screw and are only used for refrigeration in rare cases.
What is the working principle of the rotary screw air compressor?
The rotary screw compressor is one of the most extensively used technologies in modern industrial machinery. Screw compressors are the workhorse behind many industrial processes and applications, thanks to their dependability and versatility. This long-lasting technology is well-suited to a variety of demanding industry operations, without which organisations all over the world would face operational difficulties and inefficiency.
In air compressors, there are two primary compression concepts. The principle of positive displacement is one of them. This technology is used by a variety of compressors, the most common of which being screw compressors.
Operating Principles
A set of male and female rotors are located within the compressor. They'll be built differently such that when they're all twisted at the same time, air gets trapped between them. The male rotor features convex lobes, while the female rotor has concave chambers, allowing them to mesh without touching and achieve compression. As the male rotor has fewer lobes than the female, it will rotate faster, thus driving the female rotor. Unlike piston compressors, which use the same compression concept, the screw element does not have valves. As a result, it can operate at high shaft speeds without causing instability due to mechanical or volumetric losses. Screw technology may therefore combine a high flow rate with a small, space-saving design.
What are the benefits of rotary screw air compressors?
Screw compressors, being the technology of choice for a wide range of reciprocating compressor applications, have a lot to offer customer including:
Continuous operation - They don't need to be turned on and off, and they don't have a duty cycle because they can provide continuous airflow and pressurisation. This implies they can run indefinitely with little to no downtime.
Easy to maintain - Wear and tear are minimised because there are very few moving and contacting parts. Long service intervals save maintenance expenses and make routine inspections and repairs simple, quick, and painless.
Powerful performance - Screw compressors have high airflow rates and can perform at extreme temperatures, allowing them to operate in difficult environments. This implies they can readily and efficiently operate pneumatic tools and big equipment.
Energy-efficient - These long-lasting machines emit less heat and use less energy than other models since they have endured the test of time. Because of these design qualities, there is no capacity decrease over time, lowering the compressor's lifetime cost.
Low noise - The quiet operation of the devices is due to their tiny size and absence of moving parts, making them ideal for point-of-use installations.
Are screw compressors better?
To understand which one is better, the following comparison can be helpful - Screw air compressor -
- A constant supply of air
- Increased duty cycle
- Better long-term durability
- Increased overall effectiveness
- Reduced background noise
- Airflow per rated power is higher.
Reciprocating air compressor -
- Extremely high pressure demands
- Spare parts management
- Reduced duty cycle
What is the difference between the reciprocating compressor to a screw type compressor?
The mechanism by which Rotary Screw Air Compressors and Reciprocating Air Compressors compress air differs significantly.
Their distinguishing characteristics can be summed up as follows:
System design
For compressing the input air, rotary screw air compressors use a pair of meshing spiral screws known as rotors. For compressing the air, reciprocating air compressors use pistons that are moved by a crankshaft.
Components involved
Screw air compressors are not vulnerable to significant wear and tear because they only have two moving parts (screws) with a little space between them. Even in versions where the two screws come into contact with one another, there is little friction, therefore they are less prone to break down. Reciprocal air compressors, on the other hand, contain more moving parts, such as pistons, piston rings, connecting rods, and inlet-outlet valves, which makes them noisier and necessitates spare parts storage.
Temperature
Screw air compressors generate between 80 and 99 degrees Celsius of internal heat during use. Because there is no friction between the screws, heat production is reduced. With the help of a thermostatically controlled fluid circuit, the oil or lubricant employed between the rotors and casing forms a non-wearing seal that can eliminate the heat. The pistons of reciprocating air compressors operate at temperatures ranging from 150 to 200 degrees Celsius. The friction created by the movement of piston rings against the cylinder walls causes the high temperatures.
Oil filtration
Because this machine features a three-stage oil filtering system, the chances of finding leftover oil in an oil-lubricated screw air compressor are quite slim. Typically, the oil concentration is less than three particles per million (PPM).
However, because a reciprocating air compressor lacks an oil filtration mechanism, the air it produces can be more contaminated than that produced by a screw air compressor. When piston rings and oil rings deteriorate, oil can flow up to the compression side, increasing the oil concentration in the air.
Air-receiver tanks
When using a rotary screw air compressor, determining the right size of an air-receiver tank might be difficult because most of the connected applications don't require one. This machine is designed to deliver a constant stream of compressed air with no pulsation or interruption. You won't need a tank if the airflow needs of your tool is smaller than what the air compressor can provide. Piston-based compressors, on the other hand, have air-receiver tanks that store air and reduce pulsation before running the linked applications. Once the tank is filled, the equipment can be used.
Industries that use rotary screw air compressors
Screw compressors are used by many industries to increase their daily production capacity. Due to their strong design diagram and lack of a duty cycle, they are well-suited to heavy-demand industrial activities. Manufacturing sectors such as automotive, brewing, food packaging, aerospace, construction, beverage, and textile all benefit from screw air systems. Because they can withstand a wide range of working circumstances, they are appropriate for both small and large-scale operations as well.
Rotary screw air compressors are driven by two counter-rotating screws. They're usually quieter and more effective than piston engines. Rotary air compressors are utilised when huge amounts of high-pressure air are required on a daily basis for around 8 hours. Rotary screw air compressors also have extended lifespans, making them an excellent long-term investment. Because there is no metal-to-metal contact, there is less wear. Finally, these systems are generally easy to maintain.




Manufacturing
experience of
Years
Global
presence of
Countries
Sales & Distribution
network of
cities
Request a Free Quote
We will get back to you within 24 hrs
FAQs
Common questions we get asked about air compressors with our replies.
Trouble shooting questions are answered on another page, there links to other popular air compressor related pages to the right.
How air is Compressed ?
The atmospheric air enters the compressor at atmospheric pressure and leaves it as a high pressure at low volume gas . This process can be done by Piston or by Rotary.
Why Compressed Air is needed?
All process in indusries can not be done with atmostpheric pressure hence air is required to compress so that process can be been done.
volume of 0.818 m3; or 1 lb of air a volume of 13.07 ft3.
What are points to be considered for Compressor selection?
- Causing leakages causing facrors like rust and scale deposits in steel pipes
- Any resistance
- Improper selection of pressure controling devices in the system
- Moist in electro-magnetic controls
- Freezing of moisture in pneumatic conveying system
- Inaccurate moving parts
Why Quality of Compressed Air is Important?
- To reduce the running costs
- Easy maintenance at low costs
- Quick operation
Common impurities found in Compressed Air?
- Humidity
- Dust particles
- Oil mixed during the process by the compressor
- Gases, Vapours, Fumes.
- Bacteria/Viruses
Defination of Dew Point?
Dew point can be defined as the temperature at which air is fully saturated and below which water will condense.
How to dry the Compressed Air?
Compressed Air can be dried by two methods -
- Refrigeration
- Sorption
Sorption:- The air stream passes over a bed of granular desiccant which in its active state has a vapour pressure below the vapour pressure of air stream to be dried and therefore physically removes the moisture from the air stream. Sorption can be classified into Absorption and Adsorption.
Absorption:- Absorption systems use a desiccant that dissolves with the absorbed moisture. The desiccant cannot be regenerated.
Absorption:- Adsorption dryers operate by passing compressed air through a bed of desiccant material, to which the water vapour is adsorbed.. These desiccants once saturated can be regenerated and reused.
What is the basic working principle of a refrigeration Dryer?
Hot, moist air enters the refrigeration dryer through an air to air heat exchanger, where the temperature of the inlet air is reduced. This cooled air now passes through a refrigerant to air to air heat exchanger where the tempe¬rature of the air is reduced to between 2° to 5°C The cooling induces condensation and the liquid water is removed in a liquid seprator. The dry air now goes out of the dryer through the air to air heat exchange where the temperature of the air is increased to slightly below the incoming air. This is a continuous process.
The dewpoint cannot go below 2°C PDP.
What is the basic principle of the Adsorption Dryers?
There are several different types of regenerative dryers but they all conform to the same basic concept. A regenerative dryer consists of two towers filled with the desiccant. The desiccant in one bed is on stream, drying the air, while the desiccant in the other tower is being regenerated. The two towers are interlinked with switching valves so that when the desiccant in the drying tower is saturated, the valves switch the flow into the tower that has just been regenerated. This switching operation is automatic giving conti¬nuous drying.
With an adsorption dryer, very low dewpoint, down to -40°C or -60°C can be achieved.
What are Adsorbents used in the Adsorption Dryers?
- Silica Gel
- Activated Alumina
- Molecular Sieve
Application of refrigeration type air dryers?
- For general plant air, dewpoints of 2°C to 4°C are considered sufficient,
- Refrigeration type dryers use less energy and hence are lower in first and operating costs.
Our Products
Experts in the field of engineering for the compressors & vacuum pumps industry

Booster Compressor 10 To 40 HP Reciprocating
Indo-Air pressurizes the air entering the compressor at 7-13 bar up to 40 bars with the IBH series booster air compressors in its production range.

Rotary Screw 7.5 To 270 HP Lubricated
Main part of Screw Compressor is Air-end, consisting of a pair of rotors. The male motor is driven by electric motor. Suction of air though Inlet filter and suction control valve.

Reciprocating Oil Free High Pressure Water-Cooled 40 To 215 HP
The search for a reliable 100% Oil Free quality air has prompted INDO-AIR to come out with totally engineered, tested and high performance range of compessors.
Oil Free Medium Pressure Water Cooled 30 To 215 HP
The search for a reliable, 100% oil free quality air has prompted Indo-Air to introduce a totally engineered, tested and high performance range of compressors.

Reciprocating 1 To 20 HP Single-Stage Low Pressure
INDO-AIR Single-stage air compressors are designed for low pressure application. These compressors have cylinders of same size (regardless of the number of cylinders).

Reciprocating 2 To 30 HP Two-Stage Medium Pressure
INDO-AIR Two - stage air compressors are designed for medium pressure application and are made of heavy-duty components to give optimum performance.